How Does A Car’s Cooling System Work?
Published Date: September 27, 2023
The modern cooling system of a car manages to keep the temperature regulated and prevent the engine from overheating. But have you ever wondered how a car’s cooling system works? How can it maintain both warm and cool temperatures? What are the parts that make this possible? Read on to know more.
Working Of A Car Engine Cooling System
A car’s cooling system is a crucial internal combustion engine component. It maintains your car’s operating temperature by preventing overheating and regulating warm temperatures in the passenger compartment when required. The working of a car cooling system is explained below.
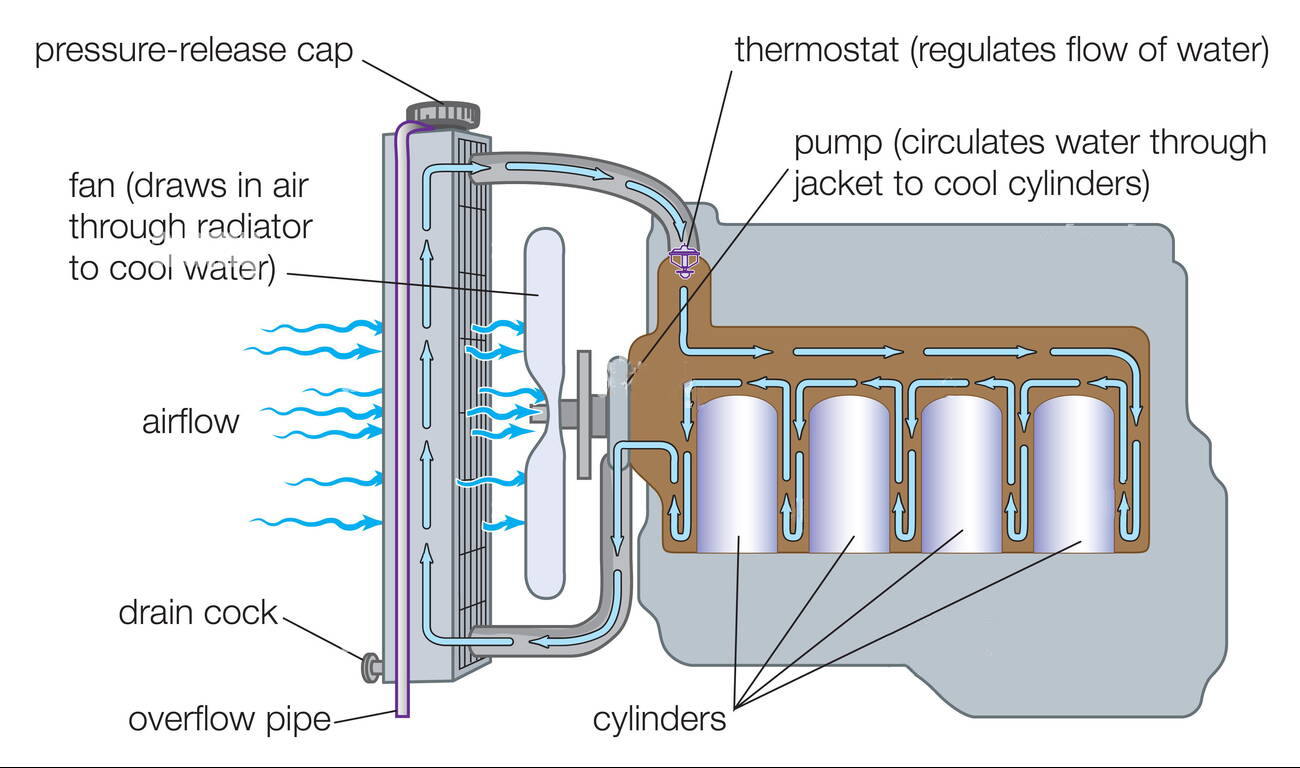
- The cooling system begins with a water pump circling coolant throughout the engine. A thermostat regulates the flow of coolant. The thermostat contains a spring-operated poppet valve. The thermostat remains closed when the engine is cold, preventing coolant flow. It only opens when the engine reaches a specific temperature (typically around 185-190 degrees Fahrenheit), allowing coolant to circulate.
- The thermostat controls the coolant’s path through the radiator. When the thermostat is closed, the coolant bypasses the radiator and flows through a bypass hose, which enables the engine to heat up without the radiator cooling.
- As the coolant circulates through the engine, it absorbs heat from the engine components. When the thermostat opens, the hot coolant flows through the radiator. Here, heat is transferred from the coolant to the radiator, and a cooling fan (either electric or belt-driven) helps dissipate this heat into the surrounding air.
- This cycle of absorbing heat from the engine, transferring it to the coolant, and then releasing it through the radiator continues maintaining the engine at its optimal operating temperature.
- The pressure release cap is a pressure relief valve and helps maintain the cooling system’s pressure. Excess coolant can escape when the system becomes pressurized due to temperature changes. When the engine cools down, coolant can be drawn back into the radiator.
In summary, the car’s cooling system relies on the circulation of coolant, controlled by a thermostat, to manage the engine’s temperature. The radiator and cooling fan play key roles in dissipating heat, ensuring the engine remains within the desired temperature range, essential for efficient and safe operation.
Components of Car Engine Cooling System
The cooling system’s main objective is to keep the engine within its ideal temperature range. It consists of the following components:
Radiator
A heat exchanger called a radiator is positioned at the front of the vehicle. It is made up of an intricate system of tiny tubes and fins. These tubes carry coolant, and air moving through the fins aids in releasing heat from the coolant.
Coolant

Water and a specific coolant solution are combined to create antifreeze known as coolant. It circulates throughout the engine and is a heat absorber, keeping it from overheating or freezing in cold weather.
Thermostat

The car thermostat is a vital cooling system component that regulates the engine temperature to ensure optimum performance and longevity. It does this by performing two primary functions:
- Warm-up: When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed to prevent coolant from flowing to the radiator. This allows the engine to heat up quickly and efficiently.
- Temperature maintenance: Once the engine reaches its optimum operating temperature, the thermostat opens to allow coolant to flow to the radiator
Rubber Hoses

Rubber hoses are a versatile and affordable solution for a variety of applications, including transferring coolant from the radiator to the engine.
Water Pump

The car water pump is a vital component of the cooling system that keeps the engine running at its optimal temperature. It is located near the front of the engine block and is typically driven by one of the engine belts.
The water pump works by circulating coolant through the engine and radiator. As the coolant flows through the engine, it absorbs heat from the combustion chambers and other hot components. The coolant then travels to the radiator, where it is cooled by the airflow.
Benefits of Car’s Cooling System
The cooling system in a car offers several important benefits, ensuring the engine operates efficiently and keeping passengers comfortable. Here are the key benefits of a car’s cooling system:
- Engine Temperature Regulation: The primary function of the cooling system is to maintain the engine’s temperature within the optimal operating range, typically around 200 degrees Fahrenheit. This prevents the engine from overheating, which can cause severe damage.
- Preventing Engine Damage: Excessive heat, reaching temperatures near 300 degrees Fahrenheit, can damage engines. The cooling system prevents the engine from reaching such high temperatures, preserving its longevity and performance.
- Passenger Comfort: While the cooling system keeps the engine from overheating, it also indirectly benefits passengers. The hot coolant from the engine is circulated to the heater core, allowing the vehicle’s heating system to provide warmth to the cabin.
- Heater Core Operation: The core is integral to the cooling system. It consists of tubes and metal layers that heat the air passing through it. This warm air is then distributed into the car’s interior by a blower motor, providing comfort to passengers during cold weather.
- Year-Round Comfort: The cooling system’s ability to regulate both engine and cabin temperature ensures passenger comfort in all weather conditions, whether keeping the engine cool in the summer or providing warmth in the winter.
In summary, a car’s cooling system not only safeguards the engine from overheating and potential damage but also plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable environment for passengers by facilitating the operation of the vehicle’s heating system. It is an essential component that contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle.
Belt-Driven Fans

Belt-driven fans generally function with a centrifugal clutch or a thermostatic clutch. The centrifugal clutch slows down the fan blades’ spinning as the engine speed increases. It allows the fan to freewheel, disconnected from the engine’s torque. It is based on the assumption that the vehicle must be moving down the road if the engine speed is high.
When a vehicle moves, air blows through the radiator, requiring lesser fan speed. Reducing fan speed reduces the engine’s load, improving fuel economy.
The thermostatic clutch has a built-in bi-metal spring that lessens torque to the fan blades when the engine is cold. As the spring heats up, it allows for the full operation of the fan blades. This reduces the fan speed as well, improving the fuel economy.
Electric Cooling Fans

Electric Cooling Fans are operated with the ECM (electronic control module), using input from the engine coolant temperature sensor. When the coolant reaches a set high temperature, the ECM turns the fan on, and vice versa when the coolant reaches a set low temperature.
Electronic fans are ideal as they save fuel by not putting a load on the engine. The ECM electronically controls the temperature and maintains optimal coolant temperature. The ECM turns the cooling fan on when the air conditioning is on.
The air conditioner condenser is placed in front of the radiator, making it vital that high-speed air continually blows through the radiator and the condenser when the air conditioner is running.
Pressure Caps
All automotive cooling systems are sealed with a pressure cap. As heat increases pressure, the pressure starts building up in a cooling system when the temperature rises. The results can be damaging if you forget to check this pressure. Pressure caps vent the cooling system of a car at a preset pressure.
Most pressure caps are set at 15 PSI (pounds per square inch) of pressure.
At 15 PSI, the pressure cap vents the pressure into the atmosphere. The pressure cap works the same as a thermostat with a bi-metal spring. This spring contracts and lifts the seal, allowing the air to escape.
A pressure cap can be placed on the radiator, or a plastic degas bottle (a reservoir). A degas bottle is placed in the engine compartment above the engine and radiator. Air rises when trapped in liquid; any air in the cooling system goes to the degas bottle and is pushed out of the pressure cap. Air can be adverse to the car seat cooling system.
Trapped air can inhibit the coolant’s flow and cause overheating, false temperature readings, and lack of heat in the passenger compartment.
The car engine’s cooling systems with the pressure cap on the radiator use an overflow tank. The overflow tank catches any coolant that escapes during pressure venting. If the radiator’s coolant level drops during the flow of the cooling system, the coolant is sucked out of the overflow tank and into the radiator.
Closing Thoughts
A car engine’s cooling system can keep the engine from self-destruction. The car’s cooling system continuously regulates the temperature according to what you want. Suffice it to say this system's breakdown or failure can be quite troublesome to deal with. Equipping yourself with an auto warranty can help you in such situations. Visit Consumera to learn about the top auto warranty companies.
FAQs
What Is The Cooling System Of A Car?
A car’s cooling system is essential to control the engine’s temperature and keep it from overheating. The cooling system helps preserve the engine’s normal operational temperature since overheating can result in severe engine damage.
What Is The Principle Of Car Cooling System?
A car’s cooling system circulates coolant to dissipate heat from the engine, which is cooled in the radiator before returning to the engine. The thermostat manages this procedure, guaranteeing the engine maintains its ideal temperature range. This mechanism keeps the engine from overheating and maintains its performance.
What Controls The Car Cooling System?
The car cooling system is controlled by mechanical components like the thermostat and water pump, electronic parts like temperature sensors, and the ECU (Engine Control Unit). These components collaborate to keep the engine’s temperature within a safe range, ensuring the engine operates efficiently and has a long lifespan.
What Causes Pressure In A Car Cooling System?
Pressure in a car’s cooling system is caused by the expansion of heated coolant as it circulates through the engine, generated by the engine’s heat due to combustion and friction. However, issues with the cooling system, such as a malfunctioning radiator or a coolant leak, can lead to improper pressure regulation.
What Water Should Be Used In A Car Cooling System?
Distilled water must be used in a car’s cooling system. Distractions, minerals, and other contaminants are removed through a distillation process to produce distilled water. It is essential to use distilled water since it guards against corrosion and mineral buildup in the cooling system, maintaining optimal operation.




